Introduction:
Maple syrup is a popular natural sweetener that is derived from the sap of maple trees. Known for its distinct flavor and rich texture, maple syrup has been used for centuries as a sweetening agent in various dishes and beverages. However, there has been some debate about its health benefits and potential drawbacks. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the nutritional composition of maple syrup, its potential health benefits, and factors to consider when incorporating it into your diet.
Nutritional Profile of Maple Syrup:
Maple syrup is primarily composed of carbohydrates, mainly in the form of sugars, including sucrose, glucose, and fructose. It also contains small amounts of minerals such as calcium, potassium, and manganese. Additionally, maple syrup provides antioxidants called polyphenols, which have been associated with various health benefits.
Potential Health Benefits of Maple Syrup:
a. Antioxidant properties: Maple syrup contains a range of polyphenols, including compounds like phenolic acids and flavonoids, which act as antioxidants in the body. These antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
b. Nutrient content: Although maple syrup is not a significant source of essential nutrients, it does provide small amounts of minerals like calcium and potassium. These minerals play important roles in bone health, nerve function, and maintaining fluid balance in the body.
c. Natural sweetener alternative: Compared to refined sugar, maple syrup is considered a more natural sweetener option. It is minimally processed and does not undergo the same level of refinement as white sugar, which retains some of its natural compounds and potential health benefits.
d. Potential anti-inflammatory effects: Some studies suggest that certain compounds found in maple syrup may possess anti-inflammatory properties. These compounds could help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to various chronic diseases.
Factors to Consider:
a. Calorie content: While maple syrup provides certain health benefits, it is important to note that it is still a concentrated source of calories. It should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
b. Glycemic index: Maple syrup has a moderate glycemic index, which means it can cause a moderate increase in blood sugar levels when consumed. Individuals with diabetes or those watching their blood sugar levels should monitor their intake and consider using alternative sweeteners with lower glycemic impact.
c. Processing and quality: Opt for high-quality maple syrup that is minimally processed and free from additives or artificial ingredients. Choose organic options whenever possible to avoid potential pesticide residues.
Incorporating Maple Syrup into a Healthy Diet:
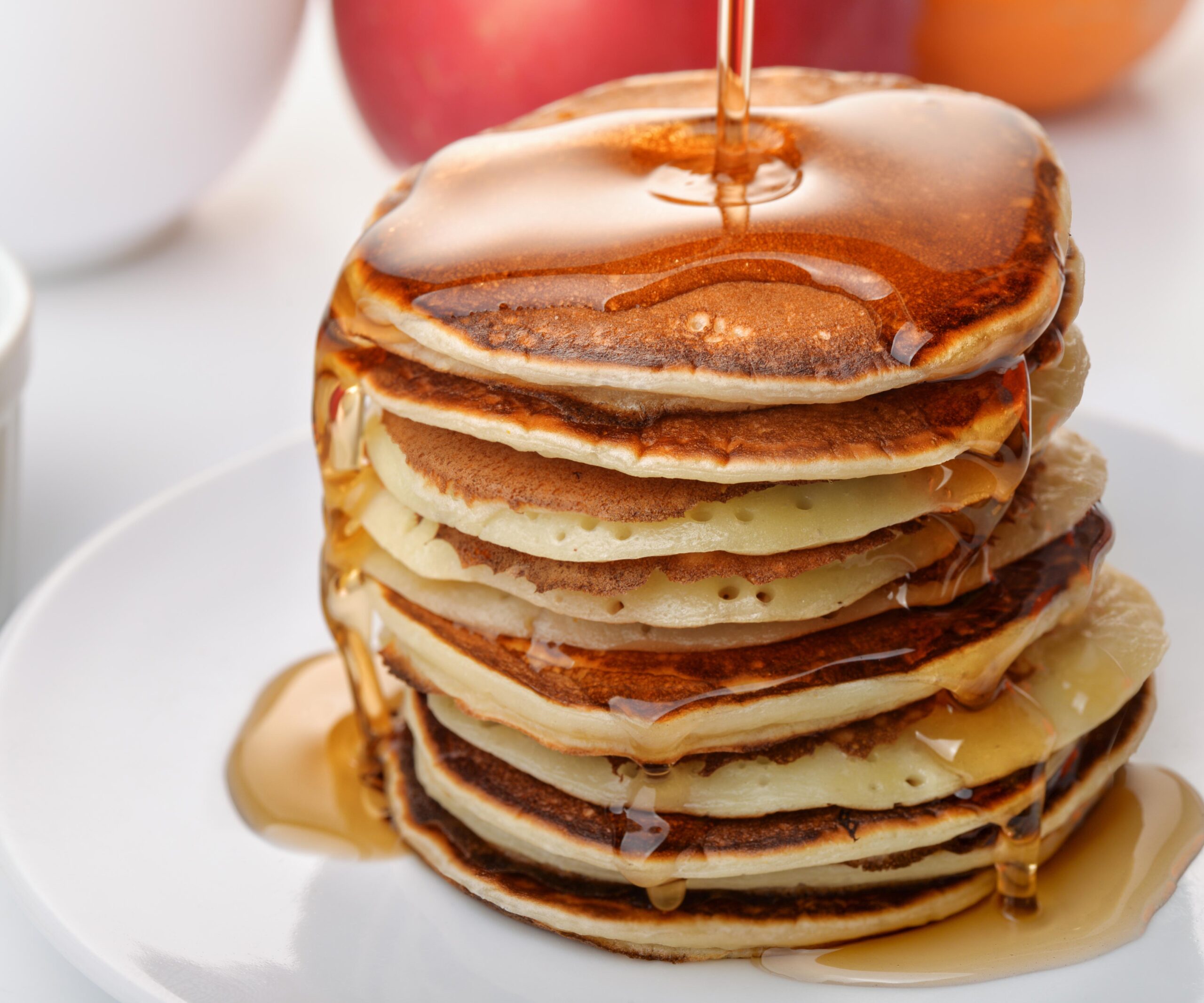
a. Moderation is key: Maple syrup should be consumed in moderation as part of a well-balanced diet. Use it sparingly as a natural sweetener in recipes, such as drizzling it over pancakes, waffles, oatmeal, or adding a touch to homemade dressings or sauces.
b. Pairing with nutritious foods: Combine maple syrup with nutrient-dense foods to enhance flavor and nutritional value. For example, use it to sweeten Greek yogurt topped with fresh fruits or as a glaze for roasted vegetables.
c. Explore maple-based products: Apart from traditional maple syrup, there are other maple-based products available, such as maple sugar or maple water. These can provide alternative ways to incorporate the flavor of maple into your diet.
Conclusion:
Maple syrup can be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet, providing a natural sweetener option with potential health benefits. However, it is important to use it in moderation and consider factors such as calorie content, glycemic index, and quality. As with any food, it is essential to consider your individual dietary needs and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure it aligns with your health goals.
- Vape Pen Kits By Vapesourcing-Unveiling the Finest Vape Pen Kits Comprehensive Review - March 26, 2024
- The Comprehensive Guide to the Benefits of Rhodiola Rosea Nootropics - October 20, 2023
- The Comprehensive Guide to the Benefits of Vegan Omega-3 - October 20, 2023